Running EMR Containers on AWS Outposts¶
Background¶
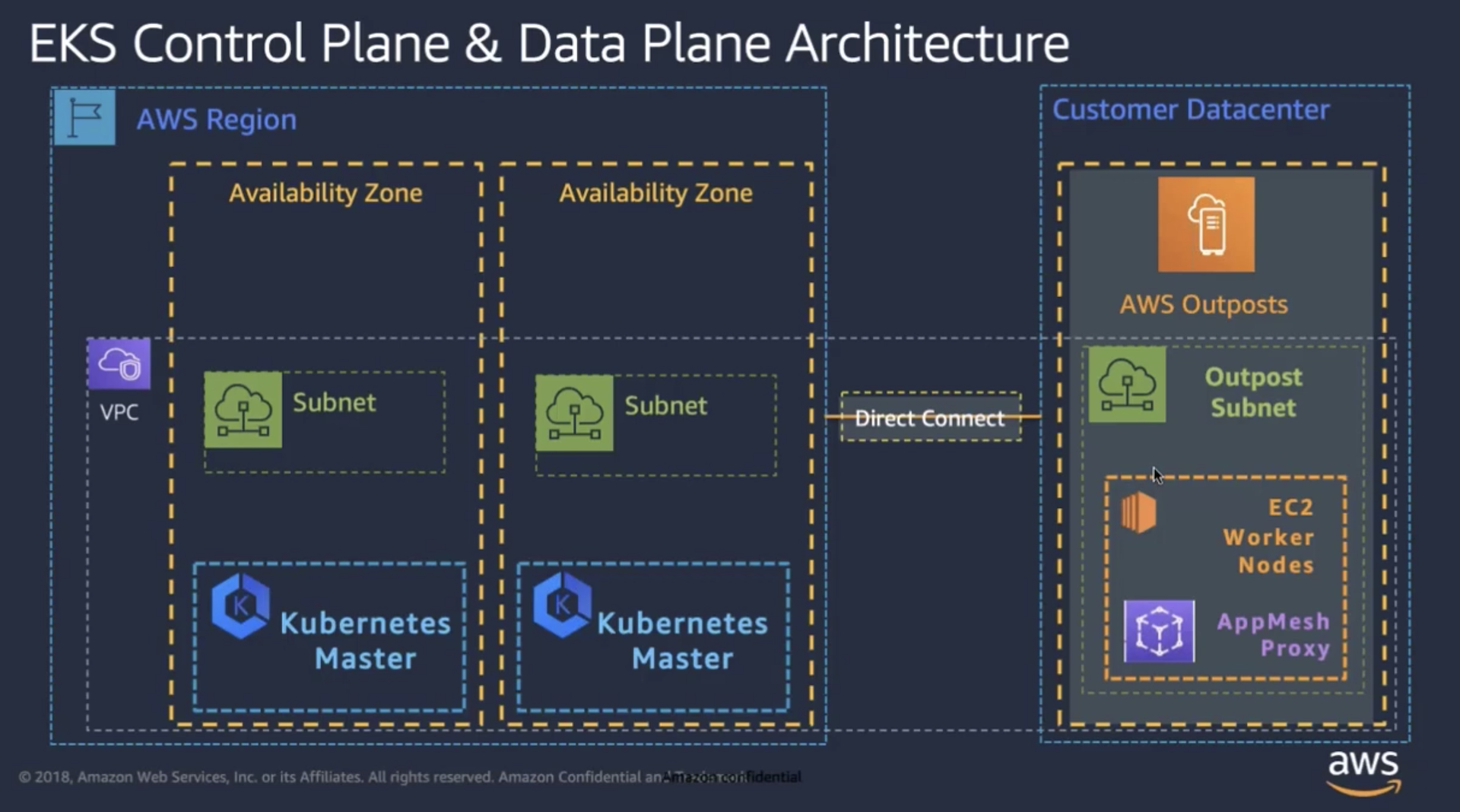
You can now run Amazon EMR container jobs on EKS clusters that are running on AWS Outposts. AWS Outposts enables native AWS services, infrastructure, and operating models in on-premises facilities. In AWS Outposts environments, you can use the same AWS APIs, tools, and infrastructure that you use in the AWS Cloud. Amazon EKS nodes on AWS Outposts is ideal for low-latency workloads that need to be run in close proximity to on-premises data and applications. For more information, see the Amazon EKS on Outposts documentation page.
This document provides the steps to set up EMR containers on AWS Outposts.
Key Considerations and Recommendations¶
- The EKS cluster on an Outpost must be created with self-managed node groups.
- Use the AWS Management Console and AWS CloudFormation to create a self-managed node group in Outposts.
- For EMR workloads, we recommend creating EKS clusters where all the worker nodes reside in the self-managed node group of Outposts.
- The Kubernetes client in the Spark driver pod creates and monitor executor pods by communicating with the EKS managed Kubernetes API server residing in the parent AWS Region. For reliable monitoring of executor pods during a job run, we also recommend having a reliable low latency link between the Outpost and the parent Region.
- AWS Fargate is not available on Outposts.
- For more information about the supported Regions, prerequisites and considerations for Amazon EKS on AWS Outposts, see the EKS on Outposts documentation page.
Infrastructure Setup¶
Setup EKS on Outposts¶
Network Setup
- Setup a VPC
aws ec2 create-vpc \
--region <us-west-2> \
--cidr-block '<10.0.0.0/16>'
In the output, take note of the VPC ID.
{
"Vpc": {
"VpcId": "vpc-123vpc",
...
}
}
- Create two subnets in the parent Region.
aws ec2 create-subnet \
--region '<us-west-2>' \
--availability-zone-id '<usw2-az1>' \
--vpc-id '<vpc-123vpc>' \
--cidr-block '<10.0.1.0/24>'
aws ec2 create-subnet \
--region '<us-west-2>' \
--availability-zone-id '<usw2-az2>' \
--vpc-id '<vpc-123vpc>' \
--cidr-block '<10.0.2.0/24>'
In the output, take note of the Subnet ID.
{
"Subnet": {
"SubnetId": "subnet-111",
...
}
}
{
"Subnet": {
"SubnetId": "subnet-222",
...
}
}
- Create a subnet in the Outpost Availability Zone. (This step is different for Outposts)
aws ec2 create-subnet \
--region '<us-west-2>' \
--availability-zone-id '<usw2-az1>' \
--outpost-arn 'arn:aws:outposts:<us-west-2>:<123456789>:outpost/<op-123op>' \
--vpc-id '<vpc-123vpc>' \
--cidr-block '<10.0.3.0/24>'
In the output, take note of the Subnet ID.
{
"Subnet": {
"SubnetId": "subnet-333outpost",
"OutpostArn": "..."
...
}
}
EKS Cluster Creation
- Create an EKS cluster using the three subnet Ids created earlier.
aws eks create-cluster \
--region '<us-west-2>' \
--name '<outposts-eks-cluster>' \
--role-arn 'arn:aws:iam::<123456789>:role/<cluster-service-role>' \
--resources-vpc-config subnetIds='<subnet-111>,<subnet-222>,<subnet-333outpost>'
- Check until the cluster status becomes active.
aws eks describe-cluster \
--region '<us-west-2>' \
--name '<outposts-eks-cluster>'
Note the values of resourcesVpcConfig.clusterSecurityGroupId and identity.oidc.issuer.
{
"cluster": {
"name": "outposts-eks-cluster",
...
"resourcesVpcConfig": {
"clusterSecurityGroupId": "sg-123clustersg",
},
"identity": {
"oidc": {
"issuer": "https://oidc.eks.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/id/oidcid"
}
},
"status": "ACTIVE",
}
}
- Add the Outposts nodes to the EKS Cluster.
At this point, eksctl cannot be used to launch self-managed node groups in Outposts. Please follow the steps listed in the self-managed nodes documentation page. In order to use the cloudformation script lised in the AWS Management Console tab, make note of the following values created in the earlier steps:
* ClusterName: <outposts-eks-cluster>
* ClusterControlPlaneSecurityGroup: <sg-123clustersg>
* Subnets: <subnet-333outpost>
Apply the aws-auth-cm config map listed on the documentation page to allow the nodes to join the cluster.
Register cluster with EMR Containers¶
Once the EKS cluster has been created and the nodes have been registered with the EKS control plane, take the following steps:
- Enable cluster access for Amazon EMR on EKS.
- Enable IAM Roles for Service Accounts (IRSA) on the EKS cluster.
- Create a job execution role.
- Update the trust policy of the job execution role.
- Grant users access to Amazon EMR on EKS.
- Register the Amazon EKS cluster with Amazon EMR.
Conclusion¶
EMR-EKS on Outposts allows users to run their big data jobs in close proximity to on-premises data and applications.