Pyspark Job submission¶
Python interpreter is bundled in the EMR containers spark image that is used to run the spark job.Python code and dependencies can be provided with the below options.
Python code self contained in a single .py file¶
To start with, in the simplest scenario - the example below shows how to submit a pi.py file that is self-contained and doesn't need any other dependencies.
Python file from S3¶
Request
pi.py used in the below request payload is from spark examples
cat > spark-python-in-s3.json << EOF
{
"name": "spark-python-in-image",
"virtualClusterId": "<virtual-cluster-id>",
"executionRoleArn": "<execution-role-arn>",
"releaseLabel": "emr-6.2.0-latest",
"jobDriver": {
"sparkSubmitJobDriver": {
"entryPoint": "s3://<s3 prefix>/pi.py",
"sparkSubmitParameters": "--conf spark.executor.instances=2 --conf spark.executor.memory=2G --conf spark.driver.memory=2G --conf spark.executor.cores=4"
}
},
"configurationOverrides": {
"applicationConfiguration": [
{
"classification": "spark-defaults",
"properties": {
"spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled":"false"
}
}
],
"monitoringConfiguration": {
"cloudWatchMonitoringConfiguration": {
"logGroupName": "/emr-containers/jobs",
"logStreamNamePrefix": "demo"
},
"s3MonitoringConfiguration": {
"logUri": "s3://joblogs"
}
}
}
}
EOF
aws emr-containers start-job-run --cli-input-json file:///Spark-Python-in-s3.json
Python file from mounted volume¶
In the below example - pi.py is placed in a mounted volume. FSx for Lustre filesystem is mounted as a Persistent Volume on the driver pod under /var/data/ and will be referenced by local:// file prefix. For more information on how to mount FSx for lustre - EMR-Containers-integration-with-FSx-for-Lustre
This approach can be used to provide spark application code and dependencies for execution. Persistent Volume mounted to the driver and executor pods lets you access the application code and dependencies with
local://prefix.
cat > spark-python-in-FSx.json <<EOF
{
"name": "spark-python-in-FSx",
"virtualClusterId": "<virtual-cluster-id>",
"executionRoleArn": "<execution-role-arn>",
"releaseLabel": "emr-6.2.0-latest",
"jobDriver": {
"sparkSubmitJobDriver": {
"entryPoint": "local:///var/data/FSxLustre-pi.py",
"sparkSubmitParameters": "--conf spark.executor.instances=2 --conf spark.executor.memory=2G --conf spark.driver.memory=2G --conf spark.executor.cores=2"
}
},
"configurationOverrides": {
"applicationConfiguration": [
{
"classification": "spark-defaults",
"properties": {
"spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled":"false",
"spark.kubernetes.driver.volumes.persistentVolumeClaim.sparkdata.options.claimName":"fsx-claim",
"spark.kubernetes.driver.volumes.persistentVolumeClaim.sparkdata.mount.path":"/var/data/",
"spark.kubernetes.driver.volumes.persistentVolumeClaim.sparkdata.mount.readOnly":"false"
}
}
],
"monitoringConfiguration": {
"cloudWatchMonitoringConfiguration": {
"logGroupName": "/emr-containers/jobs",
"logStreamNamePrefix": "demo"
},
"s3MonitoringConfiguration": {
"logUri": "s3://joblogs"
}
}
}
}
EOF
aws emr-containers start-job-run --cli-input-json file:///Spark-Python-in-Fsx.json
Python code with python dependencies¶
Info
boto3 will only work with 'Bundled as a .pex file' or with 'Custom docker image'
List of .py files¶
This is not a scalable approach as the number of dependent files can grow to a large number, and also need to manually specify all the transitive dependencies.
cat > py-files-pi.py <<EOF
from __future__ import print_function
import sys
from random import random
from operator import add
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark import SparkContext
import dependentFunc
if __name__ == "__main__":
"""
Usage: pi [partitions]
"""
spark = SparkSession.builder.getOrCreate()
sc = spark.sparkContext
partitions = int(sys.argv[1]) if len(sys.argv) > 1 else 2
n = 100000 * partitions
def f(_):
x = random() * 2 - 1
y = random() * 2 - 1
return 1 if x ** 2 + y ** 2 <= 1 else 0
count = spark.sparkContext.parallelize(range(1, n + 1), partitions).map(f).reduce(add)
dependentFunc.message()
print("Pi is roughly %f" % (4.0 * count / n))
spark.stop()
EOF
cat > dependentFunc.py <<EOF
def message():
print("Printing from inside the dependent python file")
EOF
Upload dependentFunc.py and py-files-pi.py to s3
Request:
cat > spark-python-in-s3-dependency-files << EOF
{
"name": "spark-python-in-s3-dependency-files",
"virtualClusterId": "<virtual-cluster-id>",
"executionRoleArn": "<execution-role-arn>",
"releaseLabel": "emr-6.2.0-latest",
"jobDriver": {
"sparkSubmitJobDriver": {
"entryPoint": "s3://<s3 prefix>/py-files-pi.py",
"sparkSubmitParameters": "--py-files s3://<s3 prefix>/dependentFunc.py --conf spark.executor.instances=2 --conf spark.executor.memory=2G --conf spark.driver.memory=2G --conf spark.executor.cores=2"
}
},
"configurationOverrides": {
"applicationConfiguration": [
{
"classification": "spark-defaults",
"properties": {
"spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled":"false"
}
}
],
"monitoringConfiguration": {
"cloudWatchMonitoringConfiguration": {
"logGroupName": "/emr-containers/jobs",
"logStreamNamePrefix": "demo"
},
"s3MonitoringConfiguration": {
"logUri": "s3://joblogs"
}
}
}
}
EOF
aws emr-containers start-job-run --cli-input-json file:///spark-python-in-s3-dependency-files.json
Bundled as a zip file¶
In this approach all the dependent python files are bundled as a zip file.
Each folder should have __init__.py file as documented in zip python dependencies.
Zip should be done at the top folder level and using the -r option.
zip -r pyspark-packaged-dependency-src.zip .
adding: dependent/ (stored 0%)
adding: dependent/__init__.py (stored 0%)
adding: dependent/dependentFunc.py (deflated 7%)
dependentFunc.py from earlier example has been bundled as pyspark-packaged-dependency-src.zip. Upload this file to a S3 location
cat > py-files-zip-pi.py <<EOF
from __future__ import print_function
import sys
from random import random
from operator import add
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark import SparkContext
**from dependent import dependentFunc**
if __name__ == "__main__":
"""
Usage: pi [partitions]
"""
spark = SparkSession.builder.getOrCreate()
sc = spark.sparkContext
partitions = int(sys.argv[1]) if len(sys.argv) > 1 else 2
n = 100000 * partitions
def f(_):
x = random() * 2 - 1
y = random() * 2 - 1
return 1 if x ** 2 + y ** 2 <= 1 else 0
count = spark.sparkContext.parallelize(range(1, n + 1), partitions).map(f).reduce(add)
dependentFunc.message()
print("Pi is roughly %f" % (4.0 * count / n))
spark.stop()
EOF
Request:
cat > spark-python-in-s3-dependency-zip.json <<EOF
{
"name": "spark-python-in-s3-dependency-zip",
"virtualClusterId": "<virtual-cluster-id>",
"executionRoleArn": "<execution-role-arn>",
"releaseLabel": "emr-6.2.0-latest",
"jobDriver": {
"sparkSubmitJobDriver": {
"entryPoint": "s3://<s3 prefix>/py-files-zip-pi.py",
"sparkSubmitParameters": "--py-files s3://<s3 prefix>/pyspark-packaged-dependency-src.zip --conf spark.executor.instances=2 --conf spark.executor.memory=2G --conf spark.driver.memory=2G --conf spark.executor.cores=2"
}
},
"configurationOverrides": {
"applicationConfiguration": [
{
"classification": "spark-defaults",
"properties": {
"spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled":"false"
}
}
],
"monitoringConfiguration": {
"cloudWatchMonitoringConfiguration": {
"logGroupName": "/emr-containers/jobs",
"logStreamNamePrefix": "demo"
},
"s3MonitoringConfiguration": {
"logUri": "s3://joblogs"
}
}
}
}
EOF
aws emr-containers start-job-run --cli-input-json file:///spark-python-in-s3-dependency-zip.json
Bundled as a .egg file¶
Create a folder structure as in the below screenshot with the code from the previous example - py-files-zip-pi.py, dependentFunc.py
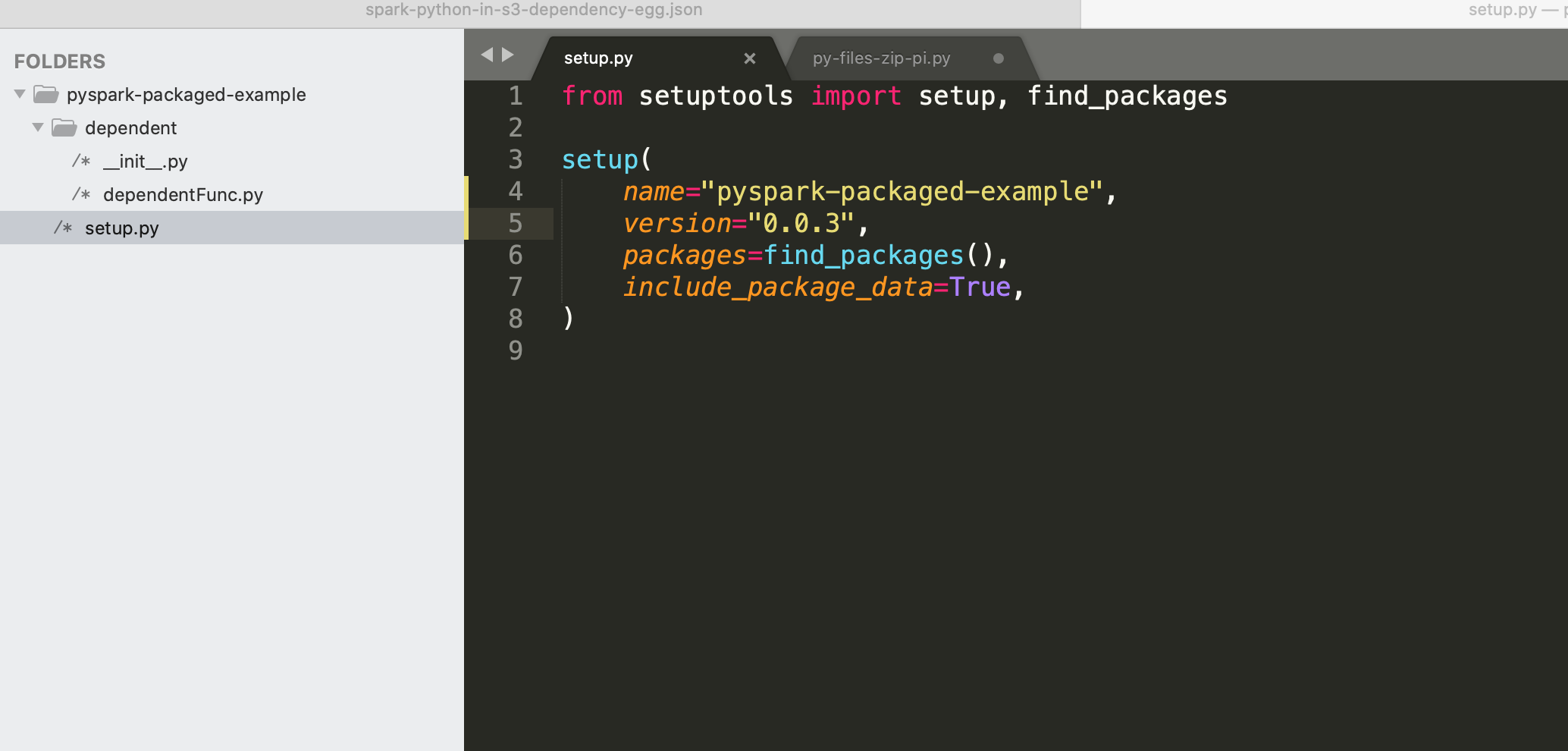
Steps to create .egg file
cd /pyspark-packaged-example
pip install setuptools
python setup.py bdist_egg
Upload dist/pyspark_packaged_example-0.0.3-py3.8.egg to a S3 location
Request:
cat > spark-python-in-s3-dependency-egg.json <<EOF
{
"name": "spark-python-in-s3-dependency-egg",
"virtualClusterId": "<virtual-cluster-id>",
"executionRoleArn": "<execution-role-arn>",
"releaseLabel": "emr-6.2.0-latest",
"jobDriver": {
"sparkSubmitJobDriver": {
"entryPoint": "s3://<s3 prefix>/py-files-zip-pi.py",
"sparkSubmitParameters": "--py-files s3://<s3 prefix>/pyspark_packaged_example-0.0.3-py3.8.egg --conf spark.executor.instances=2 --conf spark.executor.memory=2G --conf spark.driver.memory=2G --conf spark.executor.cores=2"
}
},
"configurationOverrides": {
"applicationConfiguration": [
{
"classification": "spark-defaults",
"properties": {
"spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled":"false"
}
}
],
"monitoringConfiguration": {
"cloudWatchMonitoringConfiguration": {
"logGroupName": "/emr-containers/jobs",
"logStreamNamePrefix": "demo"
},
"s3MonitoringConfiguration": {
"logUri": "s3://joblogs"
}
}
}
}
EOF
aws emr-containers start-job-run --cli-input-json file:///spark-python-in-s3-dependency-egg.json
Bundled as a .whl file¶
Create a folder structure as in the below screenshot with the code from the previous example - py-files-zip-pi.py, dependentFunc.py

Steps to create .whl file
cd /pyspark-packaged-example
`pip install wheel`
python setup.py bdist_wheel
Upload dist/pyspark_packaged_example-0.0.3-py3-none-any.whl to a s3 location
Request:
cat > spark-python-in-s3-dependency-wheel.json <<EOF
{
"name": "spark-python-in-s3-dependency-wheel",
"virtualClusterId": "<virtual-cluster-id>",
"executionRoleArn": "<execution-role-arn>",
"releaseLabel": "emr-6.2.0-latest",
"jobDriver": {
"sparkSubmitJobDriver": {
"entryPoint": "s3://<s3 prefix>/py-files-zip-pi.py",
"sparkSubmitParameters": "--py-files s3://<s3 prefix>/pyspark_packaged_example-0.0.3-py3-none-any.whl --conf spark.executor.instances=2 --conf spark.executor.memory=2G --conf spark.driver.memory=2G --conf spark.executor.cores=2"
}
},
"configurationOverrides": {
"applicationConfiguration": [
{
"classification": "spark-defaults",
"properties": {
"spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled":"false"
}
}
],
"monitoringConfiguration": {
"cloudWatchMonitoringConfiguration": {
"logGroupName": "/emr-containers/jobs",
"logStreamNamePrefix": "demo"
},
"s3MonitoringConfiguration": {
"logUri": "s3://joblogs"
}
}
}
}
EOF
aws emr-containers start-job-run --cli-input-json file:///spark-python-in-s3-dependency-wheel.json
Bundled as a .pex file¶
pex is a library for generating .pex (Python EXecutable) files which are executable Python environments.PEX files can be created as below
docker run -it -v $(pwd):/workdir python:3.7.9-buster /bin/bash #python 3.7.9 is installed in EMR 6.1.0
pip3 install pex
pex --python=python3 --inherit-path=prefer -v numpy -o numpy_dep.pex
To read more about PEX: PEX PEX documentation Tips on PEX pex packaging for pyspark
Approach 1: Using Persistent Volume - FSx for Lustre cluster
Upload numpy_dep.pex to a s3 location that is mapped to a FSx for Lustre cluster. numpy_dep.pex can be placed on any Kubernetes persistent volume and mounted to the driver pod and executor pod.
Request:
kmeans.py used in the below request is from spark examples
cat > spark-python-in-s3-pex-fsx.json << EOF
{
"name": "spark-python-in-s3-pex-fsx",
"virtualClusterId": "<virtual-cluster-id>",
"executionRoleArn": "<execution-role-arn>",
"releaseLabel": "emr-6.2.0-latest",
"jobDriver": {
"sparkSubmitJobDriver": {
"entryPoint": "s3://<s3 prefix>/kmeans.py",
"entryPointArguments": [
"s3://<s3 prefix>/kmeans_data.txt",
"2",
"3"
],
"sparkSubmitParameters": "--conf spark.executor.instances=2 --conf spark.executor.memory=2G --conf spark.driver.memory=2G --conf spark.executor.cores=2"
}
},
"configurationOverrides": {
"applicationConfiguration": [
{
"classification": "spark-defaults",
"properties": {
"spark.kubernetes.pyspark.pythonVersion":"3",
"spark.kubernetes.driverEnv.PEX_ROOT":"./tmp",
"spark.executorEnv.PEX_ROOT":"./tmp",
"spark.kubernetes.driverEnv.PEX_INHERIT_PATH":"prefer",
"spark.executorEnv.PEX_INHERIT_PATH":"prefer",
"spark.kubernetes.driverEnv.PEX_VERBOSE":"10",
"spark.kubernetes.driverEnv.PEX_PYTHON":"python3",
"spark.executorEnv.PEX_PYTHON":"python3",
"spark.pyspark.driver.python":"/var/data/numpy_dep.pex",
"spark.pyspark.python":"/var/data/numpy_dep.pex",
"spark.kubernetes.driver.volumes.persistentVolumeClaim.sparkdata.options.claimName":"fsx-claim",
"spark.kubernetes.driver.volumes.persistentVolumeClaim.sparkdata.mount.path":"/var/data/",
"spark.kubernetes.driver.volumes.persistentVolumeClaim.sparkdata.mount.readOnly":"false",
"spark.kubernetes.executor.volumes.persistentVolumeClaim.sparkdata.options.claimName":"fsx-claim",
"spark.kubernetes.executor.volumes.persistentVolumeClaim.sparkdata.mount.path":"/var/data/",
"spark.kubernetes.executor.volumes.persistentVolumeClaim.sparkdata.mount.readOnly":"false"
}
}
],
"monitoringConfiguration": {
"cloudWatchMonitoringConfiguration": {
"logGroupName": "/emr-containers/jobs",
"logStreamNamePrefix": "demo"
},
"s3MonitoringConfiguration": {
"logUri": "s3://joblogs"
}
}
}
}
aws emr-containers start-job-run --cli-input-json file:////Spark-Python-in-s3-pex-fsx.json
Approach 2: Using Custom Pod Templates
Upload numpy_dep.pex to a s3 location. Create custom pod templates for driver and executor pods. Custom pod templates allows running a command through initContainers before the main application container is created.
In this case, the command will download the numpy_dep.pex file to the /tmp/numpy_dep.pex path of the driver and executor pods.
Note: This approach is only supported for release image 5.33.0 and later or 6.3.0 and later.
Sample driver pod template YAML file:
cat > driver_pod_tenplate.yaml <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
spec:
containers:
- name: spark-kubernetes-driver
initContainers:
- name: my-init-container
image: 895885662937.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/spark/emr-5.33.0-20210323:2.4.7-amzn-1-vanilla
volumeMounts:
- name: temp-data-dir
mountPath: /tmp
command:
- sh
- -c
- aws s3api get-object --bucket <s3-bucket> --key <s3-key-prefix>/numpy_dep.pex /tmp/numpy_dep.pex && chmod u+x /tmp/numpy_dep.pex
EOF
Sample executor pod template YAML file:
cat > executor_pod_tenplate.yaml <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
spec:
containers:
- name: spark-kubernetes-executor
initContainers:
- name: my-init-container
image: 895885662937.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/spark/emr-5.33.0-20210323:2.4.7-amzn-1-vanilla
volumeMounts:
- name: temp-data-dir
mountPath: /tmp
command:
- sh
- -c
- aws s3api get-object --bucket <s3-bucket> --key <s3-key-prefix>/numpy_dep.pex /tmp/numpy_dep.pex && chmod u+x /tmp/numpy_dep.pex
EOF
Replace initContainer's image with the respective release label's container image. In this case we are using the image of release emr-5.33.0-latest.
Upload the driver and executor custom pod templates to S3
Request:
kmeans.py used in the below request is from spark examples
cat > spark-python-in-s3-pex-pod-templates.json << EOF
{
"name": "spark-python-in-s3-pex-pod-templates",
"virtualClusterId": "<virtual-cluster-id>",
"executionRoleArn": "<execution-role-arn>",
"releaseLabel": "emr-5.33.0-latest",
"jobDriver": {
"sparkSubmitJobDriver": {
"entryPoint": "s3://<s3 prefix>/kmeans.py",
"entryPointArguments": [
"s3://<s3 prefix>/kmeans_data.txt",
"2",
"3"
],
"sparkSubmitParameters": "--conf spark.executor.instances=2 --conf spark.executor.memory=2G --conf spark.driver.memory=2G --conf spark.executor.cores=2"
}
},
"configurationOverrides": {
"applicationConfiguration": [
{
"classification": "spark-defaults",
"properties": {
"spark.kubernetes.pyspark.pythonVersion":"3",
"spark.kubernetes.driverEnv.PEX_ROOT":"./tmp",
"spark.executorEnv.PEX_ROOT":"./tmp",
"spark.kubernetes.driverEnv.PEX_INHERIT_PATH":"prefer",
"spark.executorEnv.PEX_INHERIT_PATH":"prefer",
"spark.kubernetes.driverEnv.PEX_VERBOSE":"10",
"spark.kubernetes.driverEnv.PEX_PYTHON":"python3",
"spark.executorEnv.PEX_PYTHON":"python3",
"spark.pyspark.driver.python":"/tmp/numpy_dep.pex",
"spark.pyspark.python":"/tmp/numpy_dep.pex",
"spark.kubernetes.driver.podTemplateFile": "s3://<s3-prefix>/driver_pod_template.yaml",
"spark.kubernetes.executor.podTemplateFile": "s3://<s3-prefix>/executor_pod_template.yaml"
}
}
],
"monitoringConfiguration": {
"cloudWatchMonitoringConfiguration": {
"logGroupName": "/emr-containers/jobs",
"logStreamNamePrefix": "demo"
},
"s3MonitoringConfiguration": {
"logUri": "s3://joblogs"
}
}
}
}
aws emr-containers start-job-run --cli-input-json file:////Spark-Python-in-s3-pex-pod-templates.json
Point to Note:
PEX files don’t have the python interpreter bundled with it. Using the PEX env variables, we pass in the python interpreter installed in the spark driver and executor docker image.
pex vs conda-pack A pex file contain only dependent Python packages but not a Python interpreter in it while a conda-pack environment has a Python interpreter as well, so with the same Python packages a conda-pack environment is much larger than a pex file. A conda-pack environment is a tar.gz file and need to be decompressed before being used while a pex file can be used directly. If a Python interpreter exists, pex is a better option than conda-pack. However, conda-pack is the ONLY CHOICE if you need a specific version of Python interpreter which does not exist and you do not have permission to install one (e.g., when you need to use a specific version of Python interpreter with an enterprise PySpark cluster). If the pex file or conda-pack environment needs to be distributed to machines on demand, there are some overhead before running your application. With the same Python packages, a conda-pack environment has large overhead/latency than the pex file as the conda-pack environment is usually much larger and need to be decompressed before being used.
For more information - Tips on PEX
Bundled as a tar.gz file with conda-pack¶
conda-pack for spark Install conda through Miniconda Open a new terminal and execute the below commands
conda create -y -n example python=3.5 numpy
conda activate example
pip install conda-pack
conda pack -f -o numpy_environment.tar.gz
Upload numpy_environment.tar.gz to a s3 location that is mapped to a FSx for Lustre cluster. numpy_environment.tar.gz can be placed on any Kubernetes persistent volume and mounted to the driver pod and executor pod.Alternatively, S3 path for numpy_environment.tar.gz can also be passed using --py-files
Request:
{
"name": "spark-python-in-s3-conda-fsx",
"virtualClusterId": "<virtual-cluster-id>",
"executionRoleArn": "<execution-role-arn>",
"releaseLabel": "emr-6.2.0-latest",
"jobDriver": {
"sparkSubmitJobDriver": {
"entryPoint": "s3://<s3 prefix>/kmeans.py",
"entryPointArguments": [
"s3://<s3 prefix>/kmeans_data.txt",
"2",
"3"
],
"sparkSubmitParameters": "--verbose --archives /var/data/numpy_environment.tar.gz#environment --conf spark.executor.instances=2 --conf spark.executor.memory=2G --conf spark.driver.memory=2G --conf spark.executor.cores=4"
}
},
"configurationOverrides": {
"applicationConfiguration": [
{
"classification": "spark-defaults",
"properties": {
"spark.executor.instances": "3",
"spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled":"false",
"spark.files":"/var/data/numpy_environment.tar.gz#environment",
"spark.kubernetes.pyspark.pythonVersion":"3",
"spark.pyspark.driver.python":"./environment/bin/python",
"spark.pyspark.python":"./environment/bin/python",
"spark.kubernetes.driver.volumes.persistentVolumeClaim.sparkdata.options.claimName":"fsx-claim",
"spark.kubernetes.driver.volumes.persistentVolumeClaim.sparkdata.mount.path":"/var/data/",
"spark.kubernetes.driver.volumes.persistentVolumeClaim.sparkdata.mount.readOnly":"false",
"spark.kubernetes.executor.volumes.persistentVolumeClaim.sparkdata.options.claimName":"fsx-claim",
"spark.kubernetes.executor.volumes.persistentVolumeClaim.sparkdata.mount.path":"/var/data/",
"spark.kubernetes.executor.volumes.persistentVolumeClaim.sparkdata.mount.readOnly":"false"
}
}
],
"monitoringConfiguration": {
"cloudWatchMonitoringConfiguration": {
"logGroupName": "/emr-containers/jobs",
"logStreamNamePrefix": "demo"
},
"s3MonitoringConfiguration": {
"logUri": "s3://joblogs"
}
}
}
}
The above request doesn't work with spark on kubernetes
Bundled as virtual env¶
Warning
This will not work with spark on kubernetes
This feature only works with YARN - cluster mode In this implementation for YARN - the dependencies will be installed from the repository for every driver and executor. This might not be a more scalable model as per SPARK-25433. Recommended solution is to pass in the dependencies as PEX file.
Custom docker image¶
See the details in the official documentation.
Dockerfile
FROM 107292555468.dkr.ecr.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/spark/emr-6.3.0
USER root
RUN pip3 install boto3
USER hadoop:hadoop
Python code with java dependencies¶
List of packages¶
Warning
This will not work with spark on kubernetes
This feature only works with YARN - cluster mode
kafka integration example
./bin/spark-submit --packages org.apache.spark:spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.12:3.1.2
List of .jar files¶
This is not a scalable approach as the number of dependent files can grow to a large number, and also need to manually specify all the transitive dependencies.
How to find all the .jar files which belongs to given package?
- Go to Maven Repository
- Search for the package name
- Select the matching Spark and Scala version
- Copy the URL of the jar file
- Copy the URL of the jar file of all compile dependencies
Request:
cat > Spark-Python-with-jars.json << EOF
{
"name": "spark-python-with-jars",
"virtualClusterId": "<virtual-cluster-id>",
"executionRoleArn": "<execution-role-arn>",
"releaseLabel": "emr-6.2.0-latest",
"jobDriver": {
"sparkSubmitJobDriver": {
"entryPoint": "s3://<s3 prefix>/pi.py",
"sparkSubmitParameters": "--jars https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/apache/spark/spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.12/3.1.1/spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.12-3.1.1.jar,https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/apache/commons/commons-pool2/2.6.2/commons-pool2-2.6.2.jar,https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/apache/kafka/kafka-clients/2.6.0/kafka-clients-2.6.0.jar,https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/apache/spark/spark-token-provider-kafka-0-10_2.12/3.1.1/spark-token-provider-kafka-0-10_2.12-3.1.1.jar,https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/apache/spark/spark-tags_2.12/3.1.1/spark-tags_2.12-3.1.1.jar --conf spark.driver.cores=3 --conf spark.executor.memory=8G --conf spark.driver.memory=6G --conf spark.executor.cores=3"
}
},
"configurationOverrides": {
"monitoringConfiguration": {
"cloudWatchMonitoringConfiguration": {
"logGroupName": "/emr-containers/jobs",
"logStreamNamePrefix": "demo"
},
"s3MonitoringConfiguration": {
"logUri": "s3://joblogs"
}
}
}
}
EOF
aws emr-containers start-job-run --cli-input-json file:///Spark-Python-with-jars.json
Custom docker image¶
See the basics in the official documentation.
Approach 1: List of .jar files
This is not a scalable approach as the number of dependent files can grow to a large number, and also need to manually specify all the transitive dependencies.
How to find all the .jar files which belongs to given package?
- Go to Maven Repository
- Search for the package name
- Select the matching Spark and Scala version
- Copy the URL of the jar file
- Copy the URL of the jar file of all compile dependencies
Dockerfile
FROM 107292555468.dkr.ecr.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/spark/emr-6.3.0
USER root
ARG JAR_HOME=/usr/lib/spark/jars/
# Kafka
ADD https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/apache/spark/spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.12/3.1.1/spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.12-3.1.1.jar $JAR_HOME
ADD https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/apache/commons/commons-pool2/2.6.2/commons-pool2-2.6.2.jar $JAR_HOME
ADD https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/apache/kafka/kafka-clients/2.6.0/kafka-clients-2.6.0.jar $JAR_HOME
ADD https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/apache/spark/spark-token-provider-kafka-0-10_2.12/3.1.1/spark-token-provider-kafka-0-10_2.12-3.1.1.jar $JAR_HOME
ADD https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/org/apache/spark/spark-tags_2.12/3.1.1/spark-tags_2.12-3.1.1.jar $JAR_HOME
RUN chmod -R +r /usr/lib/spark/jars
USER hadoop:hadoop
Observed Behavior:
Spark automatically installs all the .jar files from /usr/lib/spark/jars/ directory. In Dockerfile we are adding these
file as root user and these file will get -rw------- permission while the original files have -rw-r--r-- permission.
EMR on EKS uses hadoop:hadoop to run spark jobs and files with -rw------- permission are hidden from this user and can
not be imported. To make these file readable for all the users run the following command chmod -R +r /usr/lib/spark/jars
and the files will have -rw-r--r-- permission.
Approach 2: List of packages
This approach is a resource intensive (min 1vCPU, 2GB RAM) solution, because it will run a dummy spark job. Scale your local or CI/CD resources according to it.
Dockerfile
FROM 107292555468.dkr.ecr.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/spark/emr-6.3.0
USER root
ARG KAFKA_PKG="org.apache.spark:spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.12:3.1.2"
RUN spark-submit run-example --packages $KAFKA_PKG --deploy-mode=client --master=local[1] SparkPi
RUN mv /root/.ivy2/jars/* /usr/lib/spark/jars/
USER hadoop:hadoop
Observed Behavior:
Spark runs ivy to get all of its dependencies (packages) when --packages are defined in the submit command.
We can run a "dummy" spark job to make spark downloads its packages. These .jars are saved in /root/.ivy2/jars/ which
we can move to /usr/lib/spark/jars/ for further use. These jars having -rw-r--r-- permission and does not require further modifications.
The advantage of this method is ivy download the dependencies of the package as well, and we needed to specify only
org.apache.spark:spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.12:3.1.2 instead of 5 jars files above.
Import of Dynamic Modules (.pyd, .so)¶
Import of dynamic modules(.pyd, .so) is disallowed when bundled as a zip
Steps to create a .so file
example.c
/* File : example.c */
#include "example.h"
unsigned int add(unsigned int a, unsigned int b)
{
printf("\n Inside add function in C library \n");
return (a+b);
}
example.h
/* File : example.h */
#include<stdio.h>
extern unsigned int add(unsigned int a, unsigned int b);
gcc -fPIC -Wall -g -c example.c
gcc -shared -fPIC -o libexample.so example.o
Upload libexample.so to a S3 location.
pyspark code to be executed - py_c_call.py
import sys
import os
from ctypes import CDLL
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
if __name__ == "__main__":
spark = SparkSession\
.builder\
.appName("py-c-so-example")\
.getOrCreate()
basedir = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__))
libpath = os.path.join(basedir, 'libexample.so')
sum_list = CDLL(libpath)
data = [(1,2),(2,3),(5,6)]
columns=["a","b"]
df = spark.sparkContext.parallelize(data).toDF(columns)
df.withColumn('total', sum_list.add(df.a,df.b)).collect()
spark.stop()
Request:
cat > spark-python-in-s3-Clib.json <<EOF
{
"name": "spark-python-in-s3-Clib",
"virtualClusterId": "<virtual-cluster-id>",
"executionRoleArn": "<execution-role-arn>",
"releaseLabel": "emr-6.2.0-latest",
"jobDriver": {
"sparkSubmitJobDriver": {
"entryPoint": "s3://<s3 prefix>/py_c_call.py",
"sparkSubmitParameters": "--files s3://<s3 prefix>/libexample.so --conf spark.executor.instances=2 --conf spark.executor.memory=2G --conf spark.driver.memory=2G --conf spark.executor.cores=2"
}
},
"configurationOverrides": {
"applicationConfiguration": [
{
"classification": "spark-defaults",
"properties": {
"spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled":"false"
}
}
],
"monitoringConfiguration": {
"cloudWatchMonitoringConfiguration": {
"logGroupName": "/emr-containers/jobs",
"logStreamNamePrefix": "demo"
},
"s3MonitoringConfiguration": {
"logUri": "s3://joblogs"
}
}
}
}
EOF
aws emr-containers start-job-run --cli-input-json file:///spark-python-in-s3-Clib.json
Configuration of interest:
--files s3://<s3 prefix>/libexample.so distributes the libexample.so to the working directory of all executors.
Dynamic modules(.pyd, .so) can also be imported by bundling within .egg (SPARK-6764), .whl and .pex files.